- 30 years experience in the field of Special Education
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Common Core Standards… What? Why? How?
January 21, 2014Dyslexia Legislation in New Jersey
August 9, 2014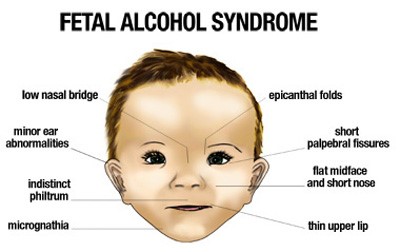 According to the National Institute on alcohol abuse common facial characteristics of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome include a low nasal bridge, minor ear abnormalities, thin upper lip, flat mid-face, short nose, epicanthal folds, indistinct philtrum and micrognathia. Along with these distinct physical characteristics, alcohol impacts cognitive processes, emotional areas and behavior. For example within the cognitive realm, typically a child with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome may have difficulty with attention, have little sense of time, difficulty following directions, memory deficits and lack appropriate social skills. Behaviorally students may demonstrate the inability to follow directions, attachment issues, overly manipulative behaviors, place others and self in harms way and acting out with over-stimulation. Cognitively, students may “just not get it”, demonstrate difficulty learning new tasks, will not exhibit the understanding of cause and effect thinking and have a poor memory.
According to the National Institute on alcohol abuse common facial characteristics of Fetal Alcohol Syndrome include a low nasal bridge, minor ear abnormalities, thin upper lip, flat mid-face, short nose, epicanthal folds, indistinct philtrum and micrognathia. Along with these distinct physical characteristics, alcohol impacts cognitive processes, emotional areas and behavior. For example within the cognitive realm, typically a child with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome may have difficulty with attention, have little sense of time, difficulty following directions, memory deficits and lack appropriate social skills. Behaviorally students may demonstrate the inability to follow directions, attachment issues, overly manipulative behaviors, place others and self in harms way and acting out with over-stimulation. Cognitively, students may “just not get it”, demonstrate difficulty learning new tasks, will not exhibit the understanding of cause and effect thinking and have a poor memory.
The CDC states that in order to meet the diagnostic criteria one must have documentation of the three predominant facial abnormalities, documentation of growth abnormalities and documentation of central nervous system dysfunction. It is helpful to know about the prenatal care and if the mom drank during pregnancy, but it is not necessary for diagnosis. Specifically for the central nervous system portion, a deficit in three or more domains must be present. These domains include cognitive, motor, executive functioning, attention, social skills, sensory and/or memory. In addition, the level of each deficit is considered
According to the Emory center for Maternal Substance Abuse and Child Development, difficulty with auditory perception, visual perception, the reception or input of information, specifically processing, organization and sequence of information, memory and the output of oral and written information. These deficits require many strategies to support learning. Typical accommodations for learning disabled students like getting the student’s attention before giving directions, using written and giving oral and gestural or pictoral directions. It is important to make sure directions are clear, concise and simple. More specific remediation when giving directions includes avoiding the use of figurative, ambiguous and idiomatic speech. One must also use the same words consistently to describe activities. Using multisensory strategies to give directions or steps to an activity, like singing, using kinesthetic strategies or motoric activities will strengthen retention and retrieval. Another important note is that typically students with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome seem to know things one day and not the next
As information retrieval is difficult many strategies are needed. Some include giving clues, such as beginning sounds of words, cueing, using a word bank or pictures of steps and checklists. Some other ways to support a student with Fetal alcohol Syndrome include making things relevant to their lives, tie new information to previous learning, using rehearsal strategies, repeating information and utilizing multi-sensory strategies.
Additionally, transitions may be particularly difficult. Cueing students through transition may ease this behavior. As distractibility is an issue, seating a student away from noisy areas, utilizing proximity to an adult and refocusing will help in this area.
According to Healthline certain drugs may help specific Fetal Alcohol Symptoms as well. Anti-anxiety and antidepressants are used for anxiousness and feelings of sadness and negativity. Stimulants may help inattention, distractibility and impulsiveness and neuroleptics are used to reduce aggression.

